Types of Non-Contact 3D Scanning Methods
Post 3D Scan
3. Laser
a. Time-of-flight: (long range, less accurate)
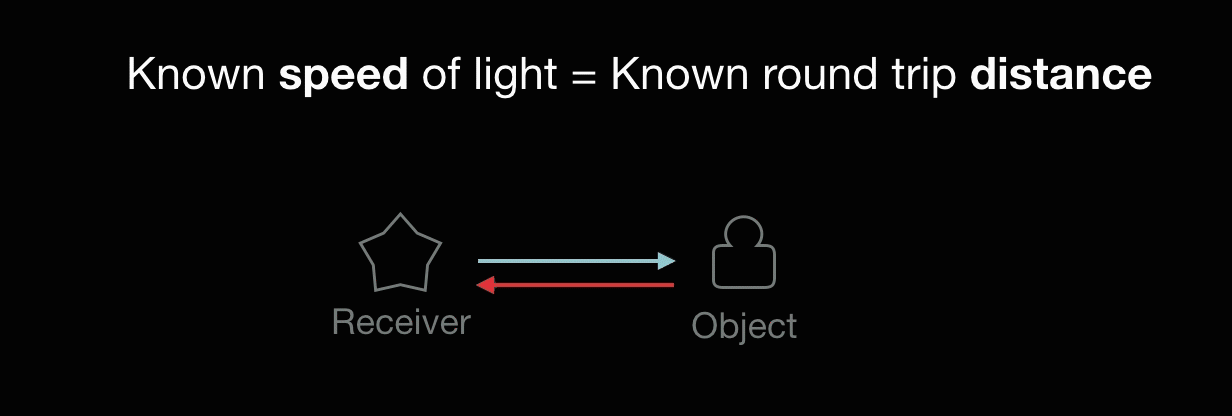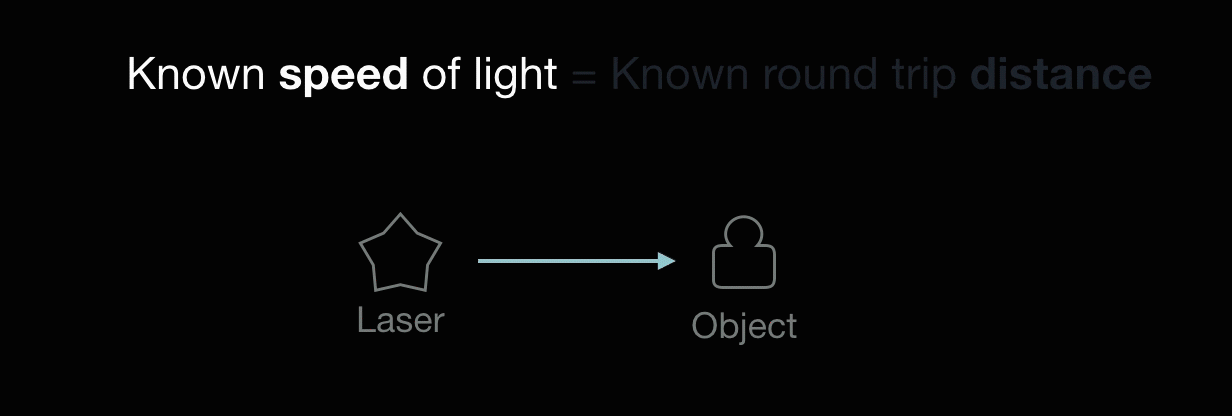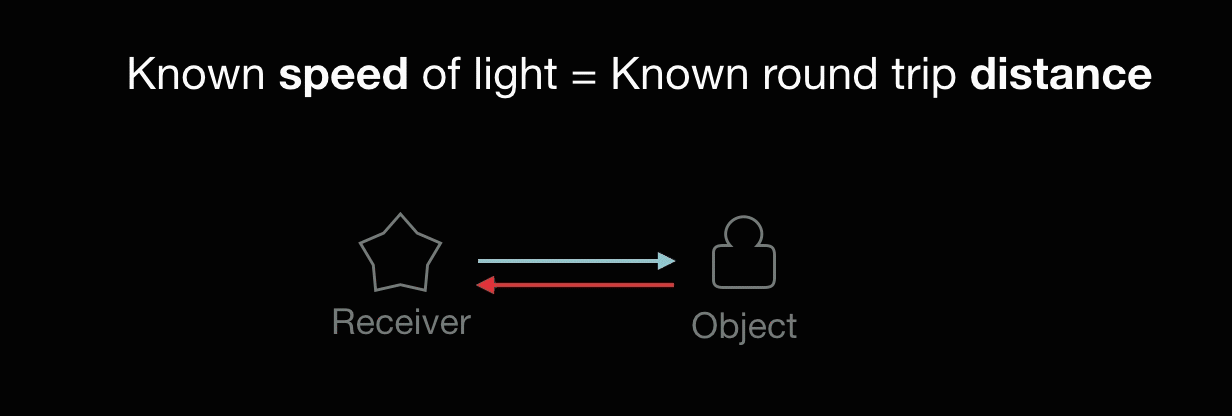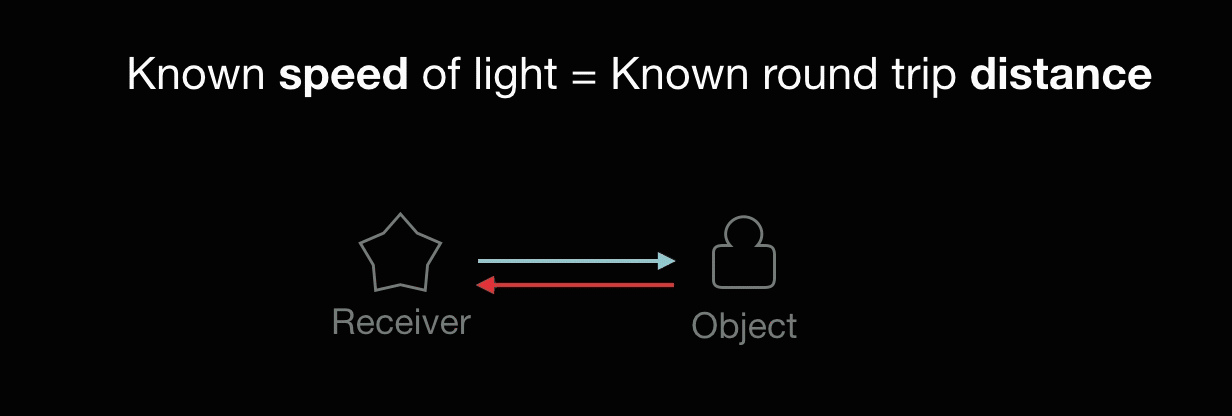
A laser emits light, and the amount of time before the reflected light is seen by a detector is measured.
Known speed of light = Known round-trip distance.
A laser emits light, and the amount of time before the reflected light is seen by a detector is measured.
Known speed of light = Known round-trip distance.
b. Triangulation: (short range, more accurate)
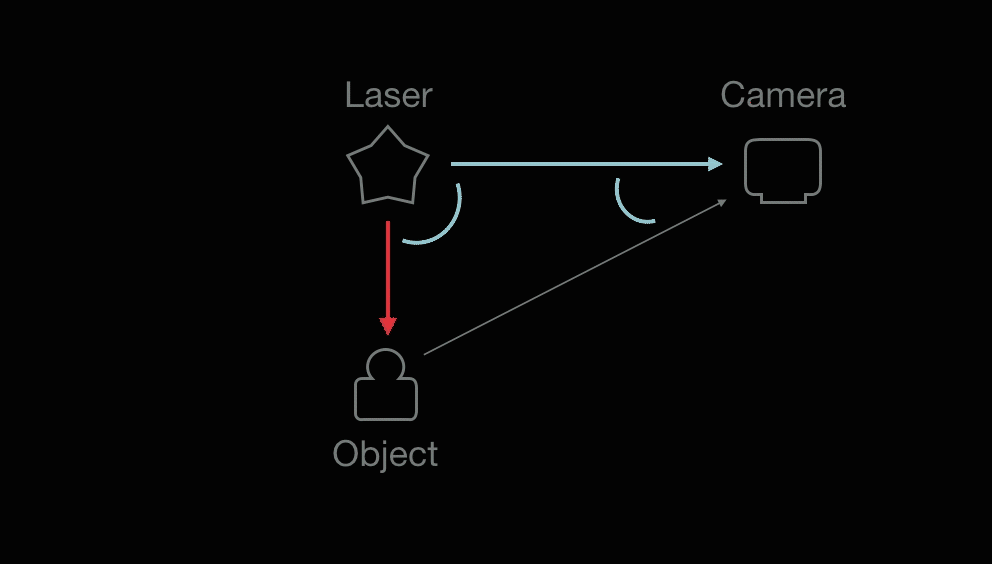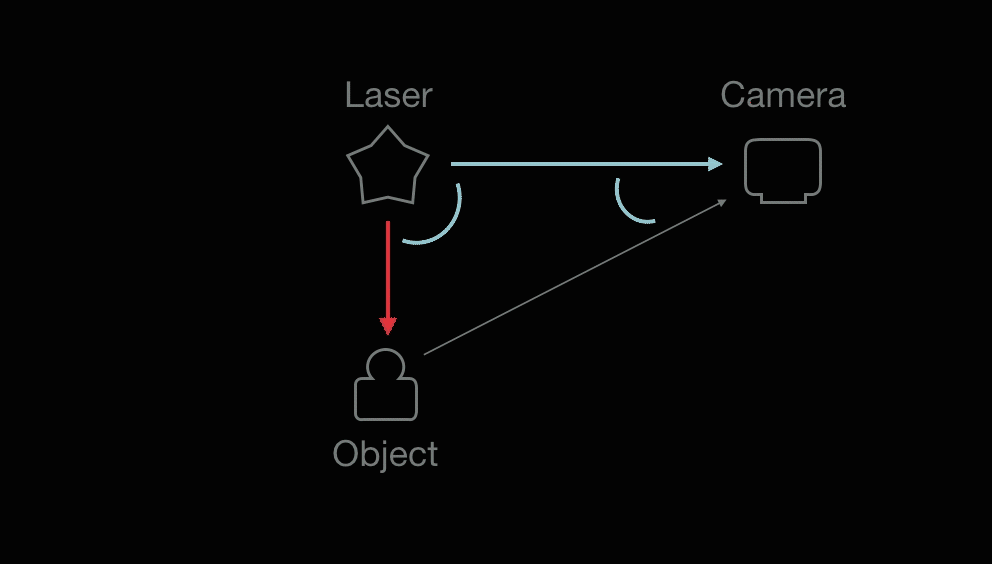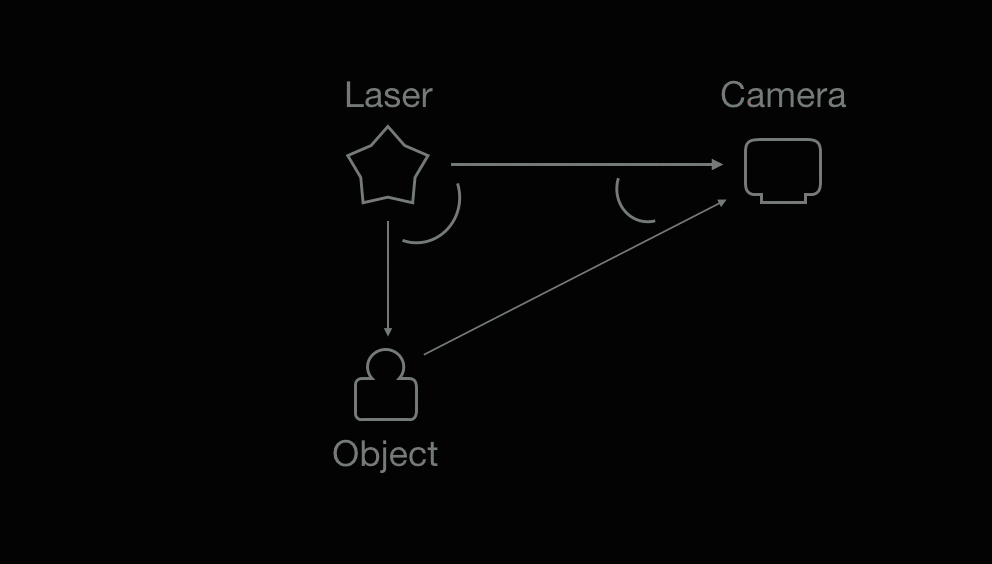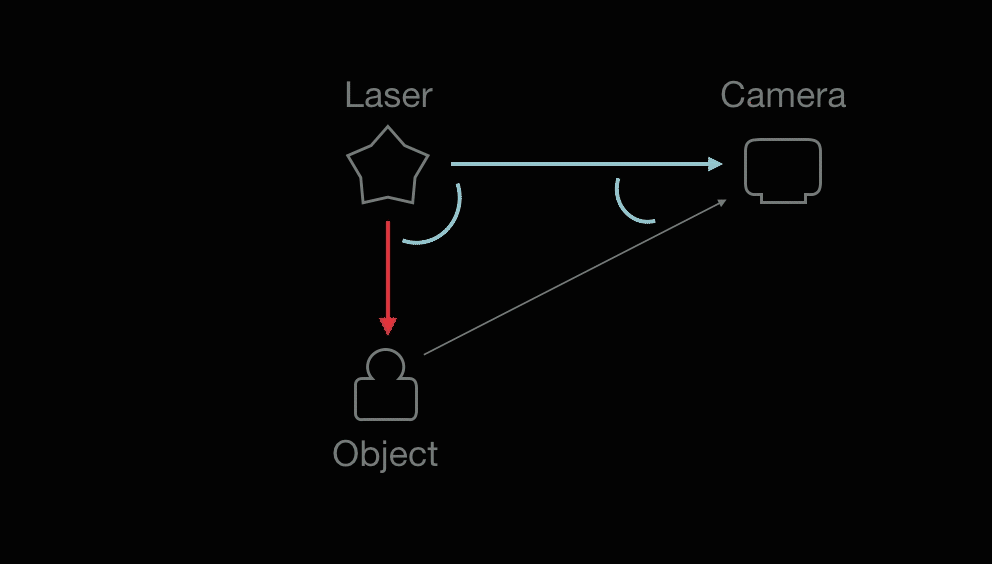
A laser emits light, and a camera is used to look for the location of the laser dot (object).
(1) The known distance between the laser emitter and the camera and (2) The angle of the laser emitter corner. (3) The angle of the camera corner can be determined by looking at the location of the laser dot in the camera's field of view. With information (1)(2)(3), the distance between the laser and object can be calculated.
A laser emits light, and a camera is used to look for the location of the laser dot (object).
(1) The known distance between the laser emitter and the camera and (2) The angle of the laser emitter corner. (3) The angle of the camera corner can be determined by looking at the location of the laser dot in the camera's field of view. With information (1)(2)(3), the distance between the laser and object can be calculated.
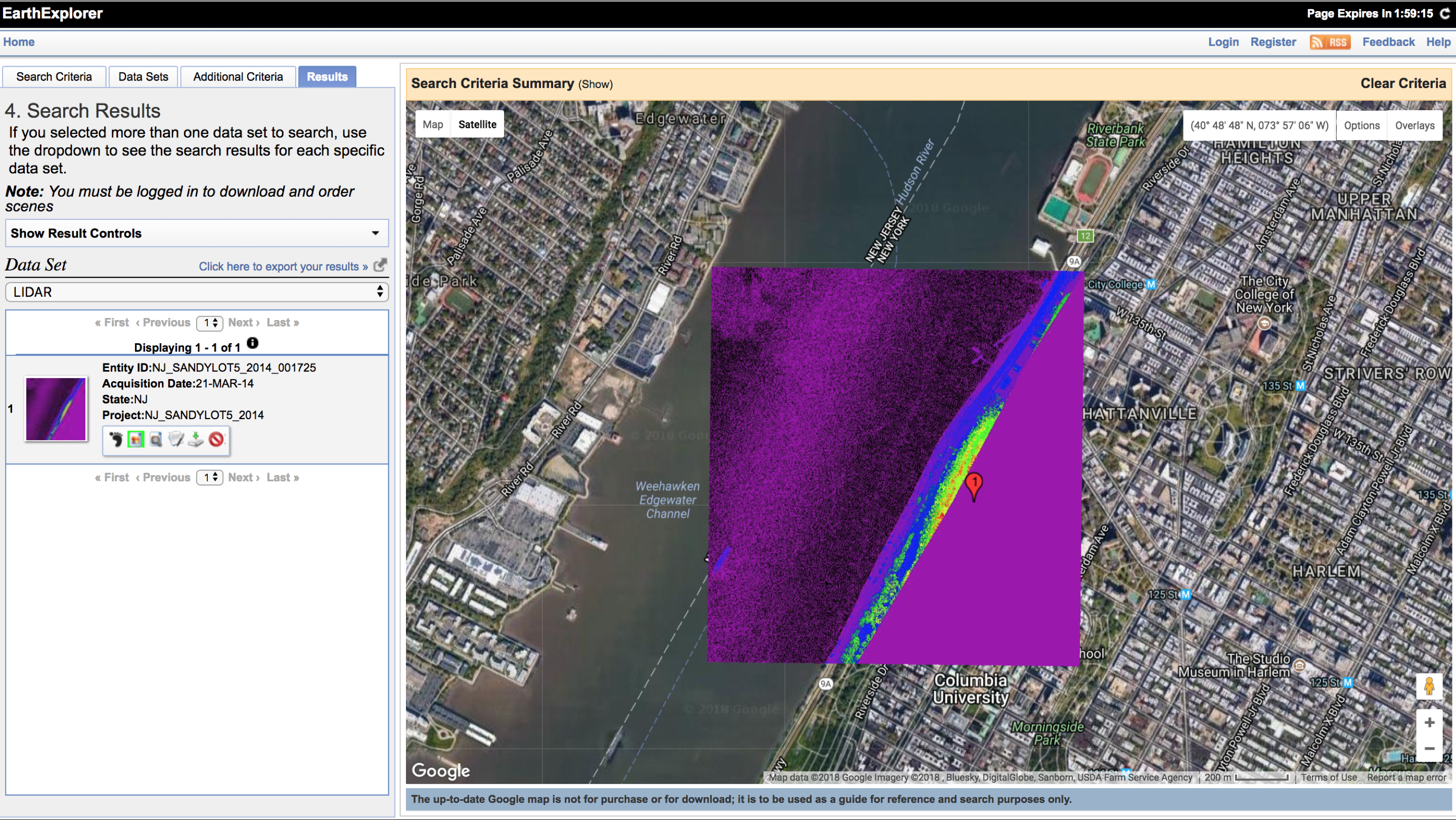
For example, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) measures how long it takes for the emitted light to return back to the sensor.
Dream Life of Driverless Cars, ScanLAB Projects for The New York Times